How to study for free in Germany, a complete guide

This article covers:
- German Free Education Concept
- Who Can Study for Free in German?
- Germany Universities Offering Free Education
- Will There Be Additional or Hidden Costs?
- Are There Any Exceptions When It Comes to Tuition Fee Waivers?
- Eligibility Requirements to Study at a Germany University
- Application Process and Other Important Matters to Successfully Study in Germany
- Health Insurance for International Students in Germany
- How to Find Accommodations in German as a Student?
- Open a Bank Account
- Before you go…
The reputation of German education is globally acclaimed, and rightfully so. Its well-structured system ensures exceptional accessibility to students, enabling them to pursue education up to the university level, irrespective of their family’s financial status. Consistency is maintained throughout all German states with a unified school and education framework. Notably, German public schools, including elementary, secondary, vocational and university institutions, typically do not impose any tuition fees.
This privilege opens its doors to international students, offering them the unique opportunity to receive a high-quality education at no tuition cost. With globally recognised degrees, numerous English-taught programs, and rich cultural experiences, Germany has positioned itself as an attractive study-abroad destination.
German Free Education Concept
In 1971, Germany’s social democrats orchestrated the eradication of tuition fees by instituting a state-funded financial assistance system. This system aimed to democratise access to quality education, extending its reach to every economic class irrespective of their financial capabilities.
By 1976, the no-fee policy was cemented legally through legislation that banned charging fees at higher education institutions. However, over the subsequent decades, this legislation would oscillate between being upheld and overturned, akin to a game of tug of war. Eventually, after several rounds of education reforms spanning decades, the final bastion, Lower Saxony, abolished its tuition fee in 2015. This marked the transition of Germany into a free-tuition nation.
As a result, both domestic and international undergraduates can now pursue their studies in Germany tuition-free, with only a minor fee required to cover administrative and other expenses each semester.
However, it is worth noting that in 2017, the state of Baden-Württemberg, located in the southwest of Germany, reintroduced tuition fees specifically for non-EU students attending public universities. As of that time, non-EU students studying at public universities in Baden-Württemberg were subject to an approximate annual tuition fee of €3,000.
Most German public universities have waived tuition fees for all students, regardless of nationality, for undergraduate and some postgraduate studies. The free education policy in Germany is deeply rooted in the country’s belief in the universal right to education. German philosophy holds education as a public good rather than a commodity. therefore, the idea is to make it accessible to as many people as possible, irrespective of their financial means.
This stance is not only generous but is also motivated by practical considerations. Firstly, it ensures that Germany has a well-educated workforce to support its highly industrialised and knowledge-based economy. Secondly, attracting international students helps to foster cultural diversity, international understanding, and exchange. This global perspective is beneficial in our increasingly connected world.
Furthermore, due to demographic changes, Germany faces a declining population and a potential future shortage of skilled workers. By attracting well-educated young people from around the world, it hopes to combat this issue. After graduation, many international students choose to remain in Germany and contribute to the local economy.
Finally, German universities also benefit from the international reputation and increased diversity that comes with having a substantial population of foreign students. It enhances the learning experience for all students by fostering an environment that encourages varied perspectives and ideas.
Who Can Study for Free in German?
In Germany, studying tuition-free is open to everyone, regardless of nationality. Whether you’re German, from another European country, or any non-European nation, you can pursue your studies in Germany without paying tuition fees. This benefit extends to nearly all study programs offered at public universities.
However, there is a minor requirement for non-EU students to keep in mind. Before arriving in Germany, they will need to obtain a residence permit. Additionally, non-EU students should plan to complete their studies within the country to continue enjoying the tuition-free privilege.
We will discuss more about how to obtain residence permits for students in the later section of this article.
Germany Universities Offering Free Education
In Germany, you can generally study for free at public universities. There are almost 300 public universities in Germany, and there are more than 1,000 study programs in total – so you have lots of options!
Some of the largest public universities include:
University of Cologne
The University of Cologne, situated in Cologne, Germany, traces its origins back to the year 1388. As one of Germany’s most esteemed and research-focused universities, it holds a prominent position in academia. It was the sixth university to be founded in Central Europe. While it faced closure in 1798, the university made a triumphant comeback and was re-established in 1919 to continue its legacy of excellence in education and research.
Ludwig Maximilians University Munich (LMU)
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, the esteemed university located in the vibrant heart of Munich. With a history dating back to its founding in 1472, LMU has earned widespread recognition as one of Europe’s foremost academic and research institutions. Throughout the years, it has been a magnet for inspired scholars and gifted students hailing from various corners of the globe. This diverse and dynamic community ensures that LMU remains at the forefront of groundbreaking ideas that continuously challenge and transform our ever-evolving world.
Goethe University Frankfurt
Goethe University Frankfurt, a prominent institution counted among the top global research universities, provides an extensive range of academic programs and hosts a diverse array of research institutes. It prides itself on fostering interdisciplinary approaches to tackle intricate challenges. Named after the illustrious Frankfurt-born polymath Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, celebrated for his remarkable contributions to literature, science, and philosophy, the university continues to uphold his spirit of excellence and innovation.
RWTH Aachen University
Situated in Aachen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, RWTH Aachen University is a renowned German public research institution. Also referred to as the Rhine-Westphalia Technical University of Aachen, Technical University of Aachen, University of Aachen, or Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, it has earned recognition under these various names.
University of Münster
Situated in the city of Münster, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, the University of Münster is a distinguished public research institution. Boasting a student population of more than 43,000 and offering an extensive selection of over 120 fields of study across 15 departments, it holds the prestigious title of Germany’s fifth-largest university. Moreover, the University of Münster stands as a prominent centre of German intellectual life, contributing significantly to the nation’s academic and research endeavours.
Ruhr University Bochum
Situated in the scenic southern hills of the central Ruhr area in Bochum, Germany, the Ruhr University Bochum is a prominent public research institution. With a significant historical distinction, it holds the honour of being the first new public university established in Germany after World War II. Its founding took place in 1962, and the university commenced its academic instruction in 1965, marking the beginning of its journey as a hub for learning, research, and academic excellence.
University of Duisburg-Essen
Located in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, the University of Duisburg-Essen stands as a prestigious public research institution. Notably, in the 2019 Times Higher Education World University Rankings, the university achieved an impressive global ranking of 194th, further cementing its reputation as a leading academic and research centre on the international stage.
Universität Hamburg
The University of Hamburg, situated in Hamburg, Germany, is a renowned public research institution. Its establishment on 28 March 1919 resulted from the amalgamation of the previous General Lecture System, the Hamburg Colonial Institute, and the Academic College. This merger marked the beginning of the university’s journey as an esteemed centre for learning and research, contributing significantly to academia and knowledge dissemination.
FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg
Established in 1743, FAU boasts a rich and storied history. As a robust research university with a global outlook, it stands as one of Germany’s largest academic institutions, accommodating 39,868 students across 263-degree programs. The university houses a dedicated academic staff of 4,000, which includes over 576 professors, facilitating a thriving learning environment.
FAU’s commitment to research excellence is evident through its impressive third-party funding of 177.6 million euros (as of 2016) and its strong network of 500 partnerships with universities worldwide. This international collaboration enriches the university’s academic landscape and fosters a diverse and inclusive learning experience.
Technical University of Munich (TUM)
The Technical University of Munich (TUM) stands proudly among Europe’s finest universities. Its unwavering dedication to research and education, coupled with a strong focus on interdisciplinary learning and nurturing young talent, exemplifies its pursuit of excellence. TUM actively fosters collaborations with global corporations and scientific organizations, reinforcing its commitment to fostering meaningful partnerships worldwide.
Notably, TUM earned the esteemed title of a University of Excellence, making it one of the pioneering universities in Germany to receive this prestigious recognition. Additionally, the university consistently secures top positions in various international rankings, reaffirming its status as one of the premier higher education institutions in Europe.
University of Würzburg
The Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg, located in Würzburg, Germany, is a distinguished public research university. Its historical significance is notable, as it holds the distinction of being one of the oldest institutions of higher learning in Germany, with its founding dating back to the year 1402. However, the university’s early journey was brief, and it underwent closure in 1415.
Will There Be Additional or Hidden Costs?
While undergraduate studies at public German universities are tuition-free, there is a nominal fee per semester for enrollment, confirmation, and administrative purposes. Generally, this fee amounts to no more than €250 (~US$290) per semester, though it may vary slightly from one university to another.
An optional “Semesterticket” is available for purchase, providing coverage for public transport expenses over a six-month period. The cost of the ticket depends on the specific Semesterticket option chosen.
Additionally, if your academic journey exceeds the standard period of study by more than four semesters, you may be subject to a long-term fee charge. This fee could amount to as much as €500 (~US$540) per semester.
Typical Living Cost in Germany as a Student
Item | Average cost per month |
Rent and utilities | 350 to 500 € |
Food and drink | 200 to 250 € |
Health insurance | 100 € |
Phone and internet | 30 € |
Leisure and hobbies | 50 to 100 € |
Depending on the city in which you study, you can manage with around 900 euros per month, with some slight variations. If you are a student requiring a visa, you will need to establish a blocked account and deposit the estimated annual cost of living before applying for the visa. Larger cities such as Munich, Frankfurt, or Hamburg are generally more expensive than smaller towns.
Are There Any Exceptions When It Comes to Tuition Fee Waivers?
Generally, you can study in Germany for free. But there are a few exceptions in which you have to pay tuition fees:
Private Universities
Studying at one of the approximately 100 private universities in Germany comes with an expectation of tuition fees. However, due to the competition they face from the more affordable public universities, private educational institutions often strive to differentiate themselves by offering specialised programs and additional benefits to ensure that students receive value for their investment. Plus, there is a possibility that you might be eligible for a scholarship, further alleviating the financial burden.
Consecutive and Non-Consecutive Master’s Programmes
Consecutive programs are those that allow you to enrol immediately after completing your Bachelor’s degree. On the other hand, non-consecutive programs typically demand that students possess post-Bachelor work experience. These non-consecutive study programs often come with tuition fees, even in public universities.
Starting in 2017, public universities in the state of Baden-Württemberg have been allowed to impose tuition fees on non-EU/EEA students. This applies to universities in cities such as Stuttgart, Karlsruhe, Mannheim, Freiburg, Heidelberg, and others. The tuition fees are set at 1,500 euros per semester, which remains considerably more affordable than in many other European countries.
Federal States (some) Tuition Fees: 500 to 650 EUR Per Semester For Secondary Degree (Zweitstudium)
This exemption does not apply if you are enrolling in a Bachelor’s program for the first time or a (consecutive) Master’s program immediately following your Bachelor’s degree. Instead, the term “secondary degree” refers to three scenarios:
- Enrolling in a non-consecutive Master’s program (as mentioned above).
- Enrolling in a Bachelor’s program when you already hold a Bachelor’s degree in another subject.
- Enrolling in a Master’s program when you already possess a Master’s degree in another subject.
Eligibility Requirements to Study at a Germany University
Each university establishes its own specific criteria for admission, which must be met by prospective students. Once you have selected the study program and university that aligns with your preferences, your first step is to thoroughly review the admission criteria and ensure that you fulfil all the necessary requirements. These criteria are among the most crucial factors considered when applying to study in Germany. Universities typically look for specific qualifications in applicants, such as a higher education entrance qualification known as
“Hochschulzugangsberechtigung” (HZB) or “Abitur.” If your school-leaving certificate is not recognized in Germany, you may need to attend a one-year preparatory course known as “Studienkolleg.”
For programs taught in English, you will be required to demonstrate proficiency in the English language through standardised tests like TOEFL or IELTS. Conversely, if your chosen program is in German, as an international student, you must provide evidence of your German language proficiency. German universities usually require language levels ranging from B2 to C1 for studies in German.
In addition to these general requirements, some universities may also mandate an aptitude test, known as “TestAS,” which assesses applicants’ capabilities in handling the requirements of their chosen degree program.
Do note that while this test certificate is not mandatory for all universities in Germany, some institutions may not include it in their admission criteria at all, while for others, it may be optional. Therefore, it is essential to carefully review the specific admission requirements of the university you intend to apply to.
Below is the procedure flow that you should follow to ensure a smooth application and admission process:
- Choose a program
- Ensure you are able to meet the criteria to study at the chosen university
- Prepare all the necessary documents that you need to submit
- Organise your finances, ensure everything is in order
- Check your health insurance policy; register if you don’t have one.
- Seek out accommodation in advance
- Apply for a visa
- Open a German bank account
Application Process and Other Important Matters to Successfully Study in Germany
The majority of applications are processed either through the platform Uni-Assist or directly via the university website. To ensure sufficient time for handling any potential missing documents, it is advisable to apply at least six weeks before the application deadline. Additionally, in some cases, applicants may be required to pay an application fee.
Typically, German universities will ask you to submit the following documents as part of your application:
- Completed application form.
- A valid passport and passport photo.
- Certified copy of your high school diploma/previous degrees.
- Relevant recognized qualifications.
- Course modules and grades (translated).
- Proof of language proficiency (depending on the program)
Student Visa and Residence Permit Application
If you are a foreigner and have obtained a letter of full admission to study at a German university, an equally recognized institution, a university of applied sciences, a college of arts and music, or any other similarly recognized higher education institution, you may be eligible for a German student visa. This visa allows you to pursue full-time university studies or preparatory measures, such as a foundation course, as part of your academic journey in Germany. However, the procedures and required documents will depend on which region you are from:
- Applicants within the European Union (including Norway, Switzerland, Iceland and Liechtenstein): If you are applying to study in Germany from within the EU (including Norway, Switzerland, Iceland and Liechtenstein) you do not need to obtain a German student visa before entering the country.
- Applicants from the US, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Israel, Japan, and South Korea: If you are from any of these countries you do not need a visa to study in Germany. However, you will need to register at the local Residents’ Registration Office and the Aliens’ Registration Office (Ausländeramt) to obtain a residence permit (Aufenthaltserlaubnis) within two weeks of arrival in the country.
- Applicants from Andorra, Brazil, El Salvador, Honduras, Monaco, San Marino or Taiwan: If you are from any of these countries, you will only need a German student visa if you plan to work before or after your degree. In this case, you should apply for the visa in your home country via your local German embassy or consulate. Both visa holders and non-visa holders will also need to apply for a residence permit within two weeks of entry. Students from Taiwan must have a passport which includes an identity card number.
- Applicants from the rest of the world: If you are from any other country not listed above, you will require a student visa for Germany. You should apply for this via the local German embassy or consulate in your home country. The typical fee for a visa is €60 (~US$70).
How to apply for a student visa to Germany
If you need a student visa for Germany, you should apply as soon as possible, and at least three months before your move to the country. To do this you’ll need to contact the local German embassy or consulate in your home country.
Y
ou may qualify for a German student visa if you plan to attend any of the following types of studies:
- Full-time academic studies.
- German language courses for academic purposes.
- State preparatory college ‘Studienkolleg’: This course is necessary for foreigners whose school-leaving certificate is not recognized in Germany. After completing the course, you will take the “Feststellungsprüfung” (assessment test). If you pass the test, you will receive a certificate known as a university entrance qualification, enabling you to apply for university admission in Germany.
- Propaedeutic course.
- Mandatory preliminary internship.
The documents you typically need for a student visa application are as follows:
- Completed application form
- Valid passport
- Two photographs
- Letter showing you’ve been accepted by a German university
- Transcript of academic record
- Certificate of German language proficiency or proof that you intend to attend a language course in Germany (if studying in German)
- Proof that you have sufficient funds to support yourself while living in Germany (€8,700 per year, which is roughly ~US$10,250)
- Certificate showing you’ve purchased health insurance
- Declaration of authenticity of documents submitted
Depending on the embassy, you may also need to show proof that you don’t have a criminal record.
Besides criminal records, another factor to take note of is having sufficient money to study in Germany.
One of the ways in which you can prove you have sufficient funds to study in Germany is by depositing a security payment into a blocked account – this means you cannot withdraw the money until after you arrive in Germany.
If your intention is to study in Germany for a period exceeding 90 days, it’s advisable to seek a National Visa specifically for studying, as opposed to a Schengen Visa. The Schengen Visa only permits a stay of up to three months in Germany.
Next, we’ll discuss the residence permit, which is a requirement in addition to your student visa.
How to apply for a residence permit
Register with the local Alien Registration Office (Bürgeramt or Einwohnermeldeamt) within two weeks of arrival. Here you must apply for a residence permit for study purposes. The documents you’ll need are similar to those needed for the visa:
- Proof of valid private or public health insurance
- Certificate of enrolment from your university
- Proof of sufficient finances
- Valid passport
- Current visa, if you have one
- Certificate of health (if applicable)
- Your tenancy agreement (if applicable)
- Biometric passport photos (if applicable)
- Residence permit fee (check the current rate beforehand to make sure you bring enough money)
Although you will already have been asked for proof of language proficiency as part of your university application, you may need to provide this information again in order to gain your residence permit. For courses taught in German, international students need to provide a TestDaf or DSH score, or, for English-taught courses, you’ll need to provide a TOEFL or IELTS score.
This residence permit is valid for two years, and, if needed, should be renewed before it expires. Residence permits initially cost €100 (~US$120) with a fee of up to €96 (~US$115) for each extension.
Students from the EU/EEA (as well as Norway, Switzerland, Iceland and Liechtenstein) do not need a residence permit but must register with the local Einwohnermeldeamt or Bürgeramt (registration authority) within a week of their arrival. You’ll need your registration document from your university for this.
EU students also need to prove they have enough money (€8,700 per year), statutory health insurance if under 30, and proficiency in their course’s language of instruction. Certain countries have bilateral agreements with Germany, which means insurance policies in the student’s home country will be applicable in Germany.
Health Insurance for International Students in Germany
Student health insurance in Germany serves a dual purpose, as it holds both practical and regulatory significance. Firstly, it provides coverage for medical assistance, ensuring your well-being in times of need. Secondly, possessing valid health insurance is a mandatory requirement for obtaining a study visa to pursue your education in Germany.
Students enrolled in degree programmes have the option to opt for public health insurance, which is available to them. However, students enrolled in preparatory or language courses, as well as those who are over the age of 30, language and preparatory course students, PhD students, and guest scientists are obliged to obtain private health insurance plans as per the requirements.
International students coming from EU countries, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Iceland, Israel, Liechtenstein, Morocco, Macedonia, Montenegro, Norway, Switzerland, Serbia, Tunisia, and Turkey are exempt from getting additional health insurance as their home country’s public insurance plans are valid in Germany. Nevertheless, it is crucial for them to check with their health insurance provider to confirm the services covered in Germany, as certain costs may not be fully covered.
However, EU/EEA students engaged in student jobs or paid internships in Germany are required to have German public health insurance.
The following categories are not eligible for the public German health insurance scheme:
- Students with health insurance from their home country that is recognized in Germany.
- Students aged 30 or above.
- Students working as freelancers or self-employed.
- Students not enrolled in degree programmes in Germany (e.g., preparatory or language courses).
- Post-graduate students and scholarship holders without a contract of employment.
- Guest scientists and researchers.
If you fall under any of the aforementioned categories, your best option is to obtain private health insurance from one of the private German student health insurance providers. A highly recommended choice is the EDUCARE24 health insurance plan offered by the well-known German health insurance company, DR-WALTER.
The benefits of choosing EDUCARE24 are as follows:
- It fulfils all the requirements for a German study visa.
- Accepted by all German Embassies/Consulates.
- Independent of student status.
- Provides health insurance without a deductible.
Easy and convenient online purchasing process, allowing you to receive your insurance certificate and all necessary documents for embassies and authorities within minutes.
EDUCARE24 offers various combinations tailored precisely to the needs of different groups:
- Language students.
- Foreign students.
- Guest scientists and PhDs.
- Interns/Trainees.
- Accompanying family members.
- With its comprehensive coverage and ease of obtaining,
EDUCARE24 is an ideal choice for all foreign students seeking private health insurance in Germany.
How to Apply for Statutory Health Insurance in German as a Student?
Techniker Krankenkasse (TK) is a highly popular public health insurer in Germany, renowned for its competitive prices and exceptional service. It is particularly favoured among both domestic and international students. For those who do not speak German, TK also offers a convenient 24/7 online service in English.
If you are seeking to obtain TK student health insurance for your stay in Germany, you need not navigate the process alone. DR-WALTER, in collaboration with TK, has developed an online consulting tool that will not only assist you in determining your insurance requirements but also enable you to apply for insurance directly.
In situations where you require private health insurance in addition to statutory health insurance, such as arriving a few days before the start of your studies, the DR-WALTER and TK tools will help identify the ideal insurance combination for your specific needs. With this user-friendly tool, securing suitable health insurance becomes a streamlined process for students in Germany.
How to Find Accommodations in German as a Student?
Germany has emerged as a highly sought-after destination for international students pursuing higher education. The country’s appeal lies in its world-class universities, rich cultural diversity, and vibrant job market, making it a top choice for students from across the globe.
Within this section, we shall delve into the various types of accommodation options accessible to international students in Germany. Additionally, we will provide useful tips and resources to aid you in finding the ideal place to reside during your studies.
Types of Accommodation for Students in German
- Student Halls of Residence (Studentenwohnheim) – Among the most popular choices for international students in Germany, student halls of residence are typically university-owned and managed accommodations offering affordable living with a sense of community. The rooms are usually single or shared, and common facilities like kitchens and bathrooms may be shared. While the living arrangements may be basic, these halls present an excellent opportunity to meet fellow students and build lasting friendships.
- Private Accommodation – Private accommodation options vary, ranging from renting a room in a shared apartment (WG) to securing an entire apartment or house. While private accommodation can be pricier than student halls of residence, it often provides more privacy and flexibility in living arrangements.
- Homestay – For international students seeking an immersive experience, homestays offer a viable option. Living with a host family provides you with a room and meals, fostering an environment to improve language skills and gain insights into German culture. However, homestays may come at a higher cost compared to other accommodation choices.
- Temporary Accommodation – If you are uncertain about your long-term living plans or need a place to stay while searching for permanent accommodation, temporary accommodation proves beneficial. This can include short-term rentals, hostels, and hotels. Although temporary options may be costlier, they provide the time required to find the perfect long-term housing solution.
Things You Need to Consider When Choosing Accommodation in German as a Student
When seeking accommodation in Germany as an international student, several essential factors should be taken into account to ensure you find the right place for your needs. Here are some of the key considerations:
- Location – The location of your accommodation is crucial. Consider its proximity to your university or college, as well as nearby amenities such as grocery stores, restaurants, public transportation, and entertainment options. The location can significantly impact your daily routine and overall experience as an international student.
- Type of Accommodation – Germany offers various accommodation options for international students, including student dormitories, shared apartments, homestays, and private apartments. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages, so consider your preferences, budget, and lifestyle to choose the most suitable accommodation type.
- Cost – Accommodation costs can vary based on the city and type of housing you select. Before making a decision, thoroughly understand all associated costs, including rent, utilities, and any additional fees or deposits. Ensure the chosen accommodation aligns with your budget.
- Roommates – If opting for shared accommodation, carefully consider potential roommates. Living with roommates can be a great way to meet new people and save on rent, but it’s crucial to find roommates with similar lifestyles, values, and habits. Discuss expectations and boundaries with potential roommates before making a decision.
- Furnishings and Amenities – Some accommodations come fully furnished, while others may require you to bring your own furniture. Know what’s included in the accommodation and ensure the provided amenities meet your needs, such as shared kitchens, private bathrooms, or laundry facilities.
- Safety and Security – Prioritise safety and security when selecting accommodation. Understand the safety measures in place, including access control, fire safety, and emergency procedures. Research the area’s crime rate and talk to current residents for insight into the neighbourhood’s safety.
- Lease Length – Consider the length of the lease before signing a rental agreement. Some accommodations may require a minimum lease length, while others offer more flexible options. Ensure the lease aligns with your future plans and needs.
Open a Bank Account
A significant number of international students opt to open a bank account in Germany, particularly when planning to stay for extended periods. Having a German bank account becomes essential as it facilitates seamless payment processing, rent payments, and easy purchases, including electronics. Opening a bank account in Germany as an international student proves convenient and cost-effective compared to using one’s account from their home country. While online account opening is now available, many students prefer to wait until they arrive in Germany to initiate the process.
To open a bank account as an international student in Germany, you will need the following documents:
- Filled-out application form.
- Your valid passport and current German residence permit.
- Proof of registration/current address.
- Proof of income/employment.
- Proof of student status (if you want to open a student account).
- Initial deposit amount (depending on the financial institution).
- SCHUFA credit rating (applicable to some banks only).
Conclusion
With proper planning and preparation, studying in Germany opens doors to a truly enriching and economical experience. Beyond the pursuit of high-quality education, this opportunity allows you to immerse yourself in a new culture, embrace diverse perspectives, and broaden your horizons in ways that extend far beyond the classroom.
Germany’s renowned universities, coupled with the country’s welcoming atmosphere, provide a nurturing environment for personal growth and academic excellence. By seizing this chance to study in Germany, you can develop valuable skills, forge lifelong friendships with peers from all corners of the globe, and foster a deeper understanding of the world.
Embracing a new language, navigating through the bustling cities and quaint towns, and delving into the rich history and vibrant traditions of Germany, you will find yourself captivated by the cultural treasures this country has to offer. The diverse landscapes, from majestic mountains to serene lakes, provide an ideal backdrop for exploration and adventure.
Moreover, Germany’s strong commitment to research and innovation offers boundless opportunities for those eager to contribute to cutting-edge advancements and discoveries in their respective fields. Engaging in hands-on learning experiences, collaborating with leading experts, and participating in renowned research projects can propel your academic journey to new heights.
As you embark on this journey, remember to embrace the challenges with an open mind and a spirit of resilience. Embrace the opportunity to step outside your comfort zone, as it is in these moments of adaptation and growth that you will uncover new facets of yourself.
From the picturesque landscapes of the Black Forest to the vibrant cultural scenes in Berlin, Germany you with an array of experiences waiting to be embraced. So, embrace the opportunity to study in Germany, and you will find yourself enriched not only academically but also as an individual on an unforgettable journey of discovery and personal transformation.
Before you go…
Once the bank account is successfully opened, that account often becomes the financial cornerstone for the students’ daily transactions, rent payments, tuition fees, and living expenses. However, transferring money from the home country to this newly minted account can pose a challenge. This is where Instarem, a trusted money remittance service, can step in to streamline the process.
Instarem offers an easy-to-use, secure, and efficient platform for international money transfers. Whether you’re a student from India, the Philippines, or any other part of the world, you can use Instarem to swiftly transfer funds from your home country to your new bank account in Germany.
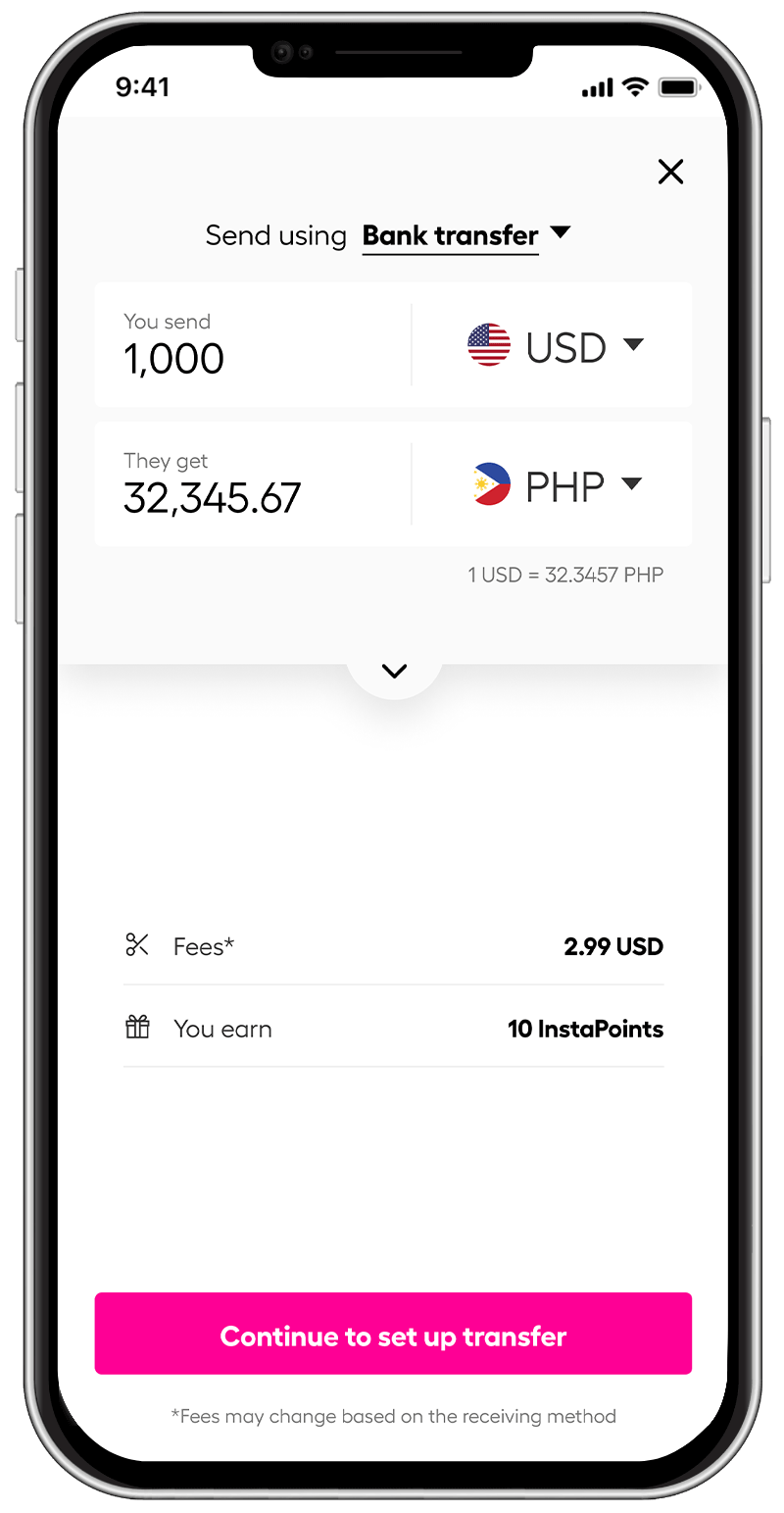
*rates are for display purposes only.
The service is renowned for its competitive exchange rates, transparency, and minimal fees, ensuring you get the most value out of every transfer.
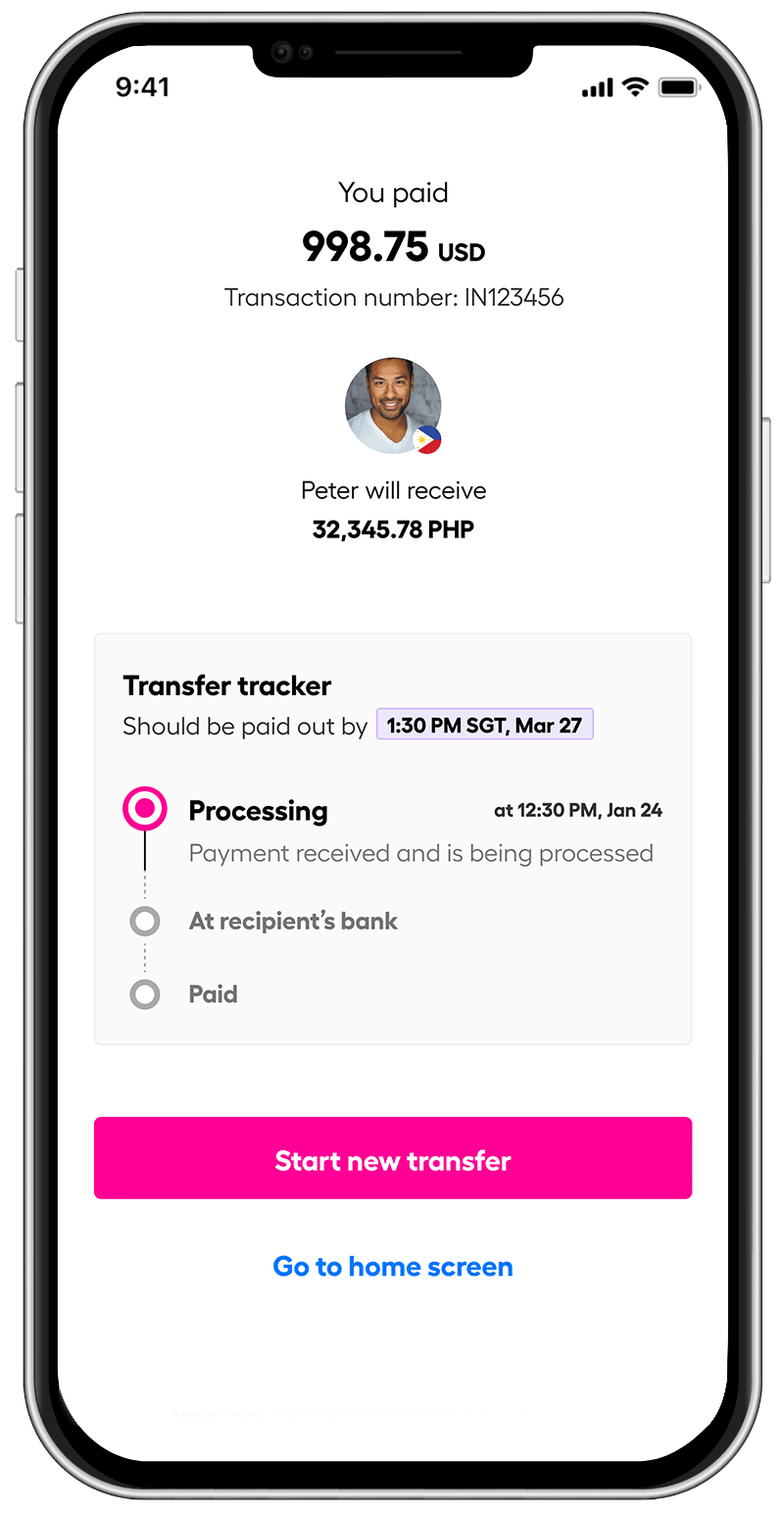
Moreover, with its real-time tracking features and instant notifications, students can stay updated on their transactions, giving them peace of mind.
By leveraging Instarem’s digital platform, international students can easily manage their finances and focus on their studies and life in Germany, without worrying about the logistics of international money transfers.
Feel free to download the app or sign up here!
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. All details are accurate at the time of publishing. Instarem has no affiliation or relationship with products or vendors mentioned.